Duolingo

About: "Duolingo is a free language-learning platform that includes a language-learning website and app, as well as a digital language proficiency assessment exam. Duolingo is ad-free and offers all its language courses free of charge. As of February 2016, the language-learning website and app offer 54 different language courses across 23 languages; with 28 additional courses in development. The app is available on iOS, Android and Windows 8 and 10 platforms with over 120 million registered users across the world." (from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duolingo)
App Analysis (iOS v. 4.6.0)
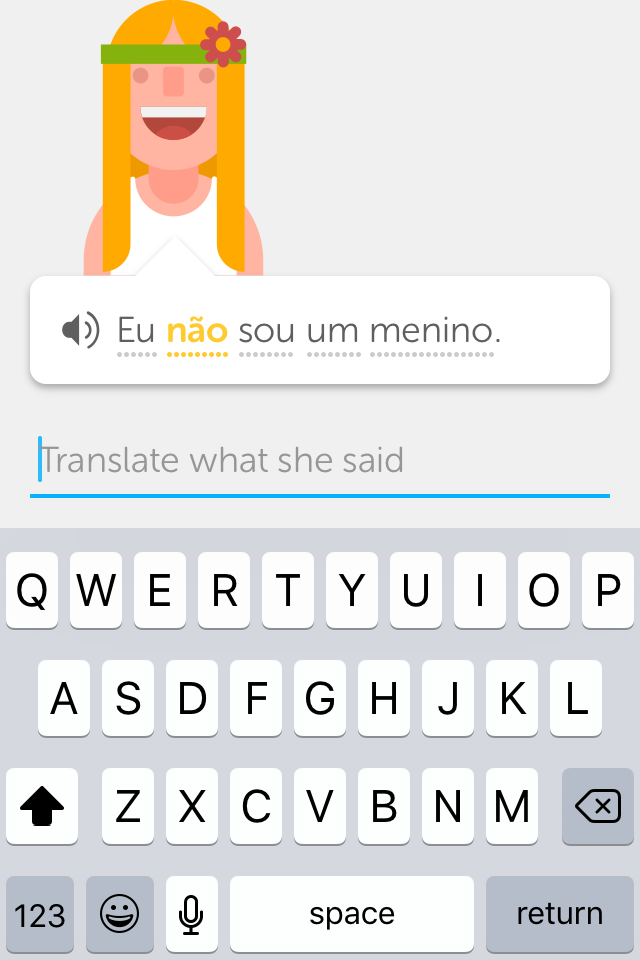
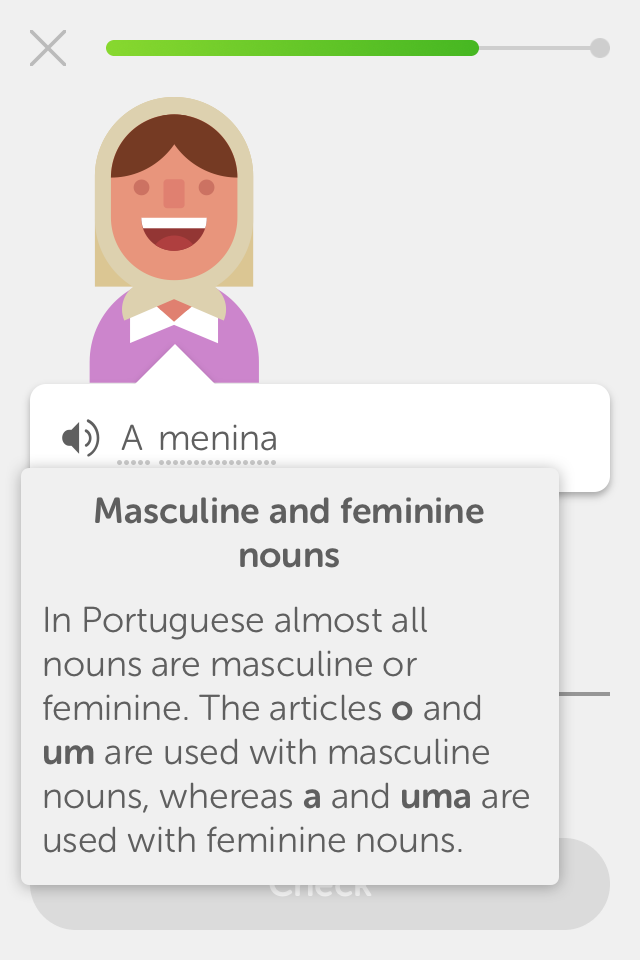
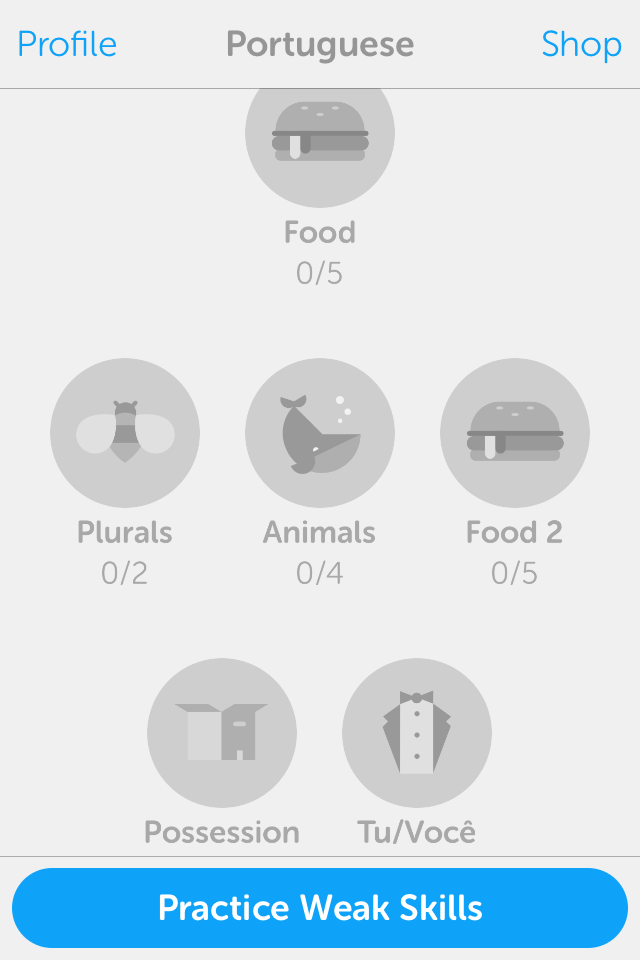
Screen-shots of the initial screens of the app
Learning
Duolingo mainly consists of a series of mini-games that introduce single words or sentences as the user progresses. It is highly anchored in the right/wrong binary, that is: users advance within the course as far as their answers are correct. Mostly, all new content is introduced through translations, therefore choosing the right answer means finding the accurate translation. As a result, users will become highly trained at associating words in their target languages with words in their native ones, which is not the same as becomeing fluent speakers in their target languages.
Easy games, with little relevance, mixed with dense, short grammar explanations
-
 Speaking:
Users are rarely prompted to speak words/sentences in the target language.
Speaking:
Users are rarely prompted to speak words/sentences in the target language.
-
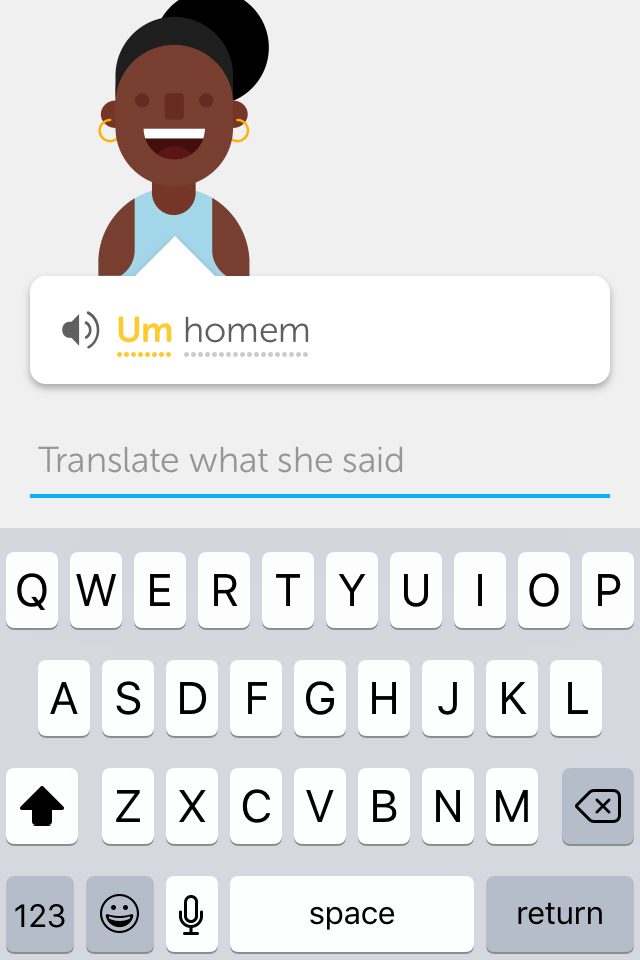
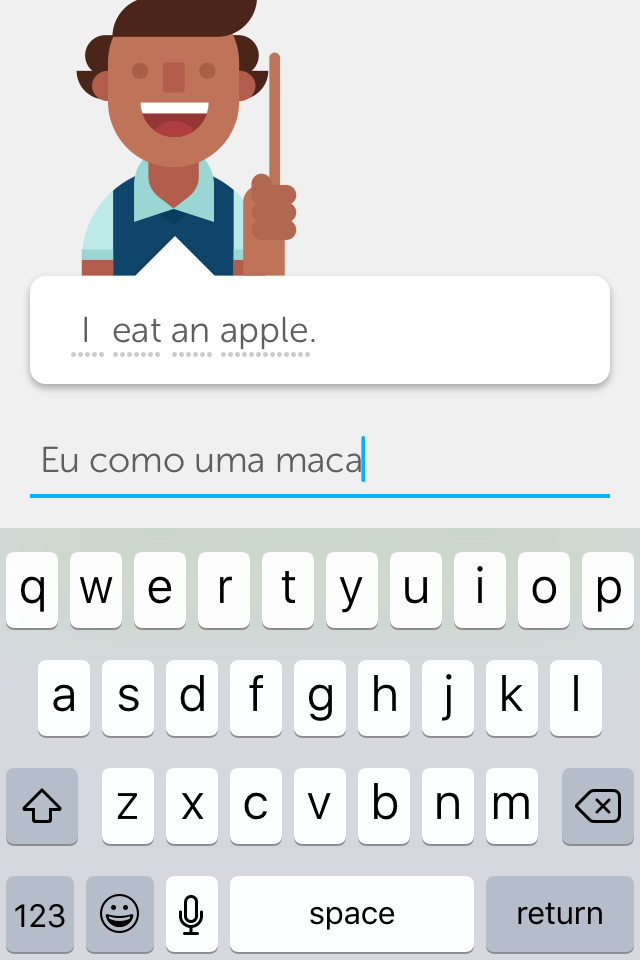
 Content:
The first lesson introduces words such as 'man', 'woman', 'bread', and 'apple'. The course is structured in different topics, which are either vocabulary-related ('animals, 'fooda') or grammar-related ('plurals', 'tu / você'). 'Phrases' is one of these topics, meaning that most times, new content is introduced on a single-word base.
Content:
The first lesson introduces words such as 'man', 'woman', 'bread', and 'apple'. The course is structured in different topics, which are either vocabulary-related ('animals, 'fooda') or grammar-related ('plurals', 'tu / você'). 'Phrases' is one of these topics, meaning that most times, new content is introduced on a single-word base.
-
 Estimated duration:
In the first lesson, only a few words were introduced: 'the', 'a', 'boy/girl', 'man/woman', 'eat', 'drink', 'water'). Acquiring fluency at this rate would probably take up to years.
Estimated duration:
In the first lesson, only a few words were introduced: 'the', 'a', 'boy/girl', 'man/woman', 'eat', 'drink', 'water'). Acquiring fluency at this rate would probably take up to years.
-
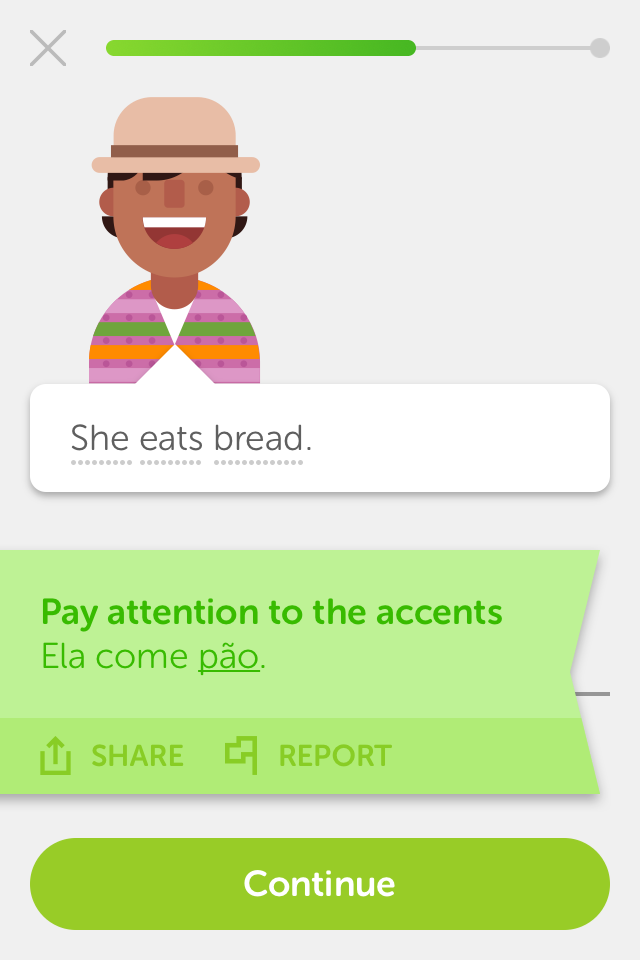
 Relevance:
Sentences such as 'She eats bread' and 'I'm not a boy' are introduced in the first lesson, even though they are not nearly as relevant as self-introductory sentences, for example, such as 'My name is____' or 'I am from ____'.
Relevance:
Sentences such as 'She eats bread' and 'I'm not a boy' are introduced in the first lesson, even though they are not nearly as relevant as self-introductory sentences, for example, such as 'My name is____' or 'I am from ____'.
-
 Focus:
Having to continuously press the continue button and often type in words can be distracting.
Focus:
Having to continuously press the continue button and often type in words can be distracting.
-
 Right:
Correct answers makes some of the items on the screen become green while sound is played.
Right:
Correct answers makes some of the items on the screen become green while sound is played.
-
 Wrong:
The progress bar shrinks and more exercises are assigned when users give 'wrong' answers.
Wrong:
The progress bar shrinks and more exercises are assigned when users give 'wrong' answers.
-
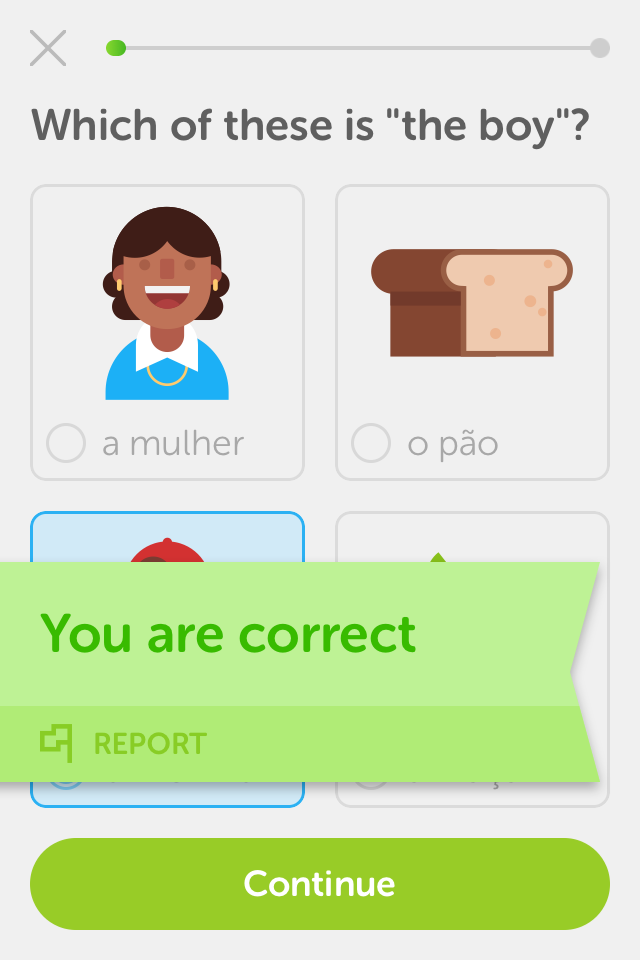
 Challenge:
The games are initialy very easy and sometimes even the pictures give away the answers.
Challenge:
The games are initialy very easy and sometimes even the pictures give away the answers.
-
 Metaphor:
Duolingo compares language learning to the life and growth of a living animal.
Metaphor:
Duolingo compares language learning to the life and growth of a living animal.
-
 Metacognition:
Duolingo rarely/never attempts to teach/discuss best learning practices/strategies.
Metacognition:
Duolingo rarely/never attempts to teach/discuss best learning practices/strategies.
-
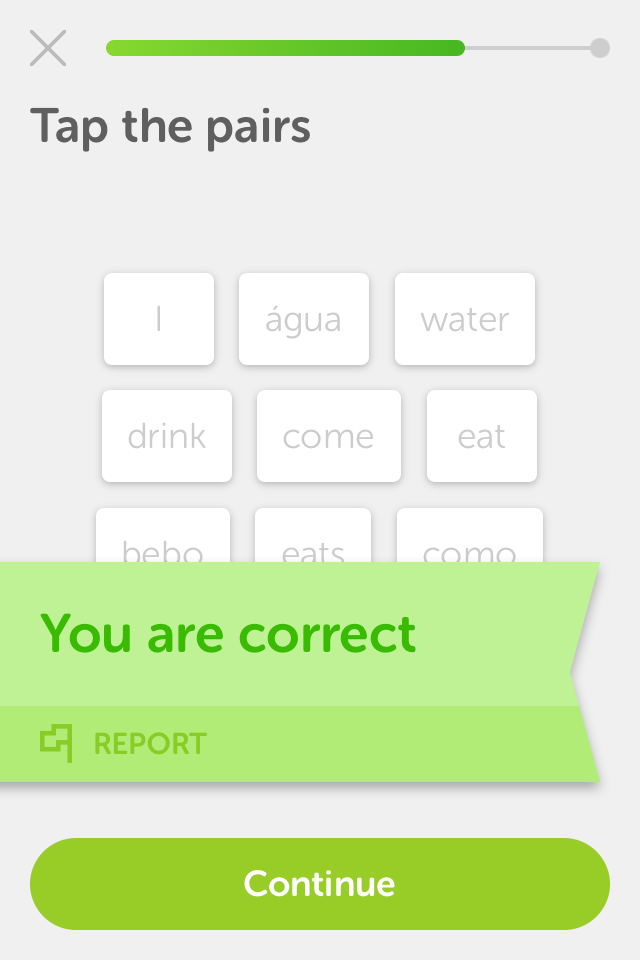
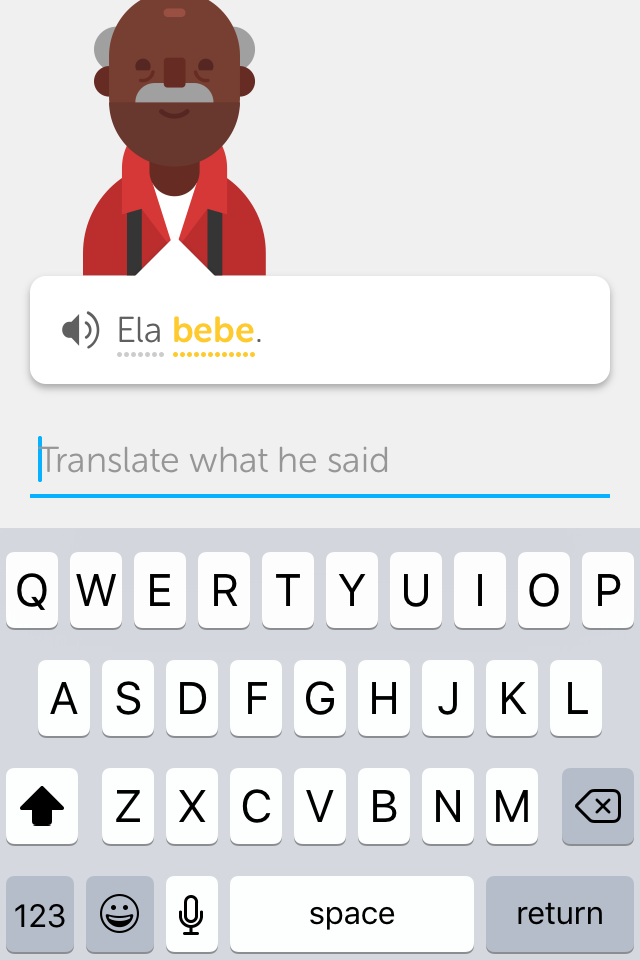
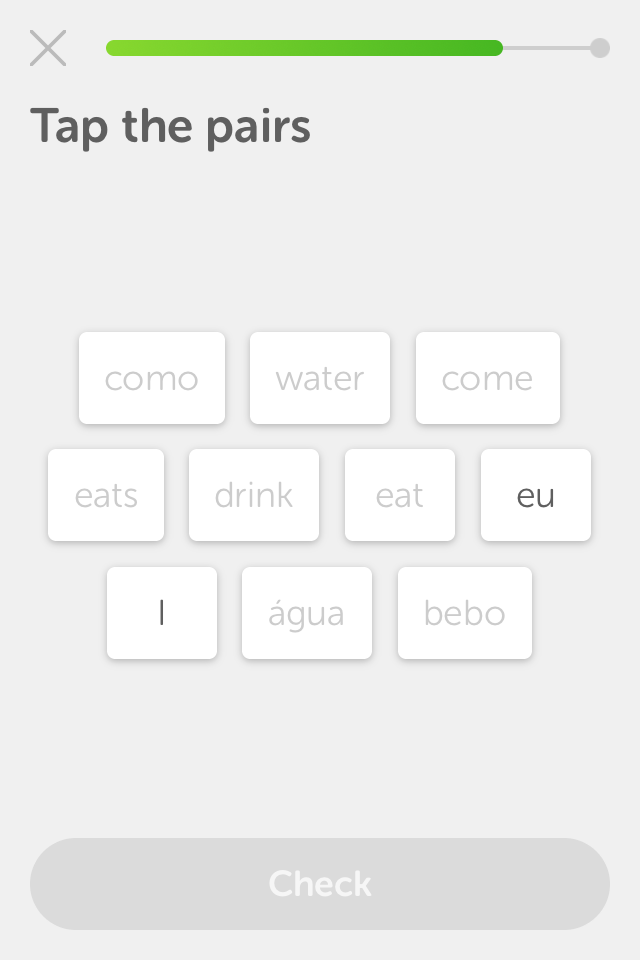
 Translation:
Sometimes, translating single words can produce wrong/oversimplified associations. For example: verbs in different English conjugations ('eat/eats') are not always equivalent to their Portuguese counterparts ('como/come').
Translation:
Sometimes, translating single words can produce wrong/oversimplified associations. For example: verbs in different English conjugations ('eat/eats') are not always equivalent to their Portuguese counterparts ('como/come').
Self-Efficacy tools
One of Duolingo's main strenghts is the amount of design features created to keep the language learning process happening. A variety of tools help users create and maintain their habits and, therefore improve their self-efficacy skills.
Daily goals, strength bars, structured content and day streaks.
-
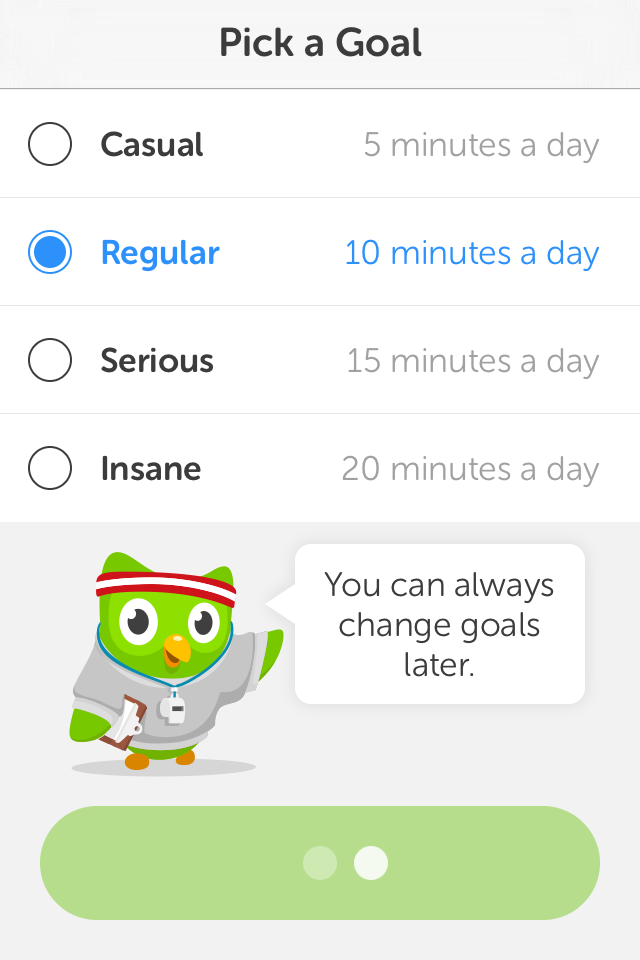
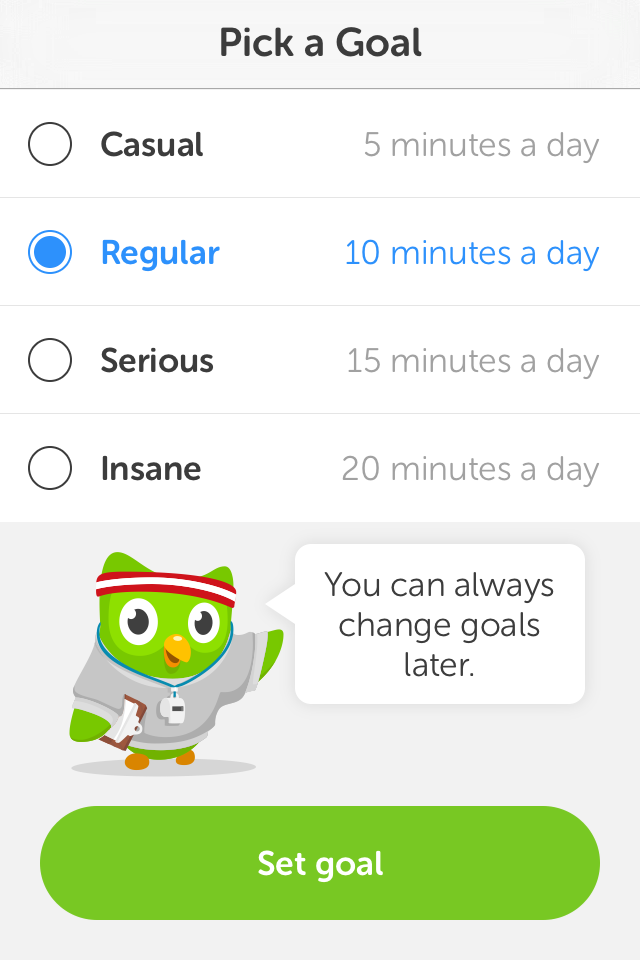
 Pick a goal:
The app can adapt to how much time/effort users intend to devote to learn a language.
Pick a goal:
The app can adapt to how much time/effort users intend to devote to learn a language.
-
 Are you a beginner?:
Users can be placed in more advanced levels based on their prior knowledge.
Are you a beginner?:
Users can be placed in more advanced levels based on their prior knowledge.
-
 Topics:
Users can decide which content they want to learn. App keeps control of options and needs.
Topics:
Users can decide which content they want to learn. App keeps control of options and needs.
-
 Weak skills:
Duolingo takes note of each user's 'weak skills' and prompts them to practice those skills.
Weak skills:
Duolingo takes note of each user's 'weak skills' and prompts them to practice those skills.
-
 Strength bar:
It features in a very clear way which topics are most/least strong in the user's memory.
Strength bar:
It features in a very clear way which topics are most/least strong in the user's memory.
-
 (#) days streak:
The app counts for how many days users have been accomplishing their daily goals.
(#) days streak:
The app counts for how many days users have been accomplishing their daily goals.
Usability
Audio output
Audio is used as exercise prompts (for example, you hear a voice saying 'Hello' and you have to match its Portuguese translation, 'Olá'). Also, when you select an answer, the app speaks the word you chose. That being said, none of the observed exercises were particularly or exclusively designed to build the users' listening or pronunciation skills.
-
 Non-native accents:
Sometimes, words are pronounced an accent that sounded Spanish.
Non-native accents:
Sometimes, words are pronounced an accent that sounded Spanish.
-
 Multiple voices:
Typical male/female voices from different people are played throughout the course.
Multiple voices:
Typical male/female voices from different people are played throughout the course.
-
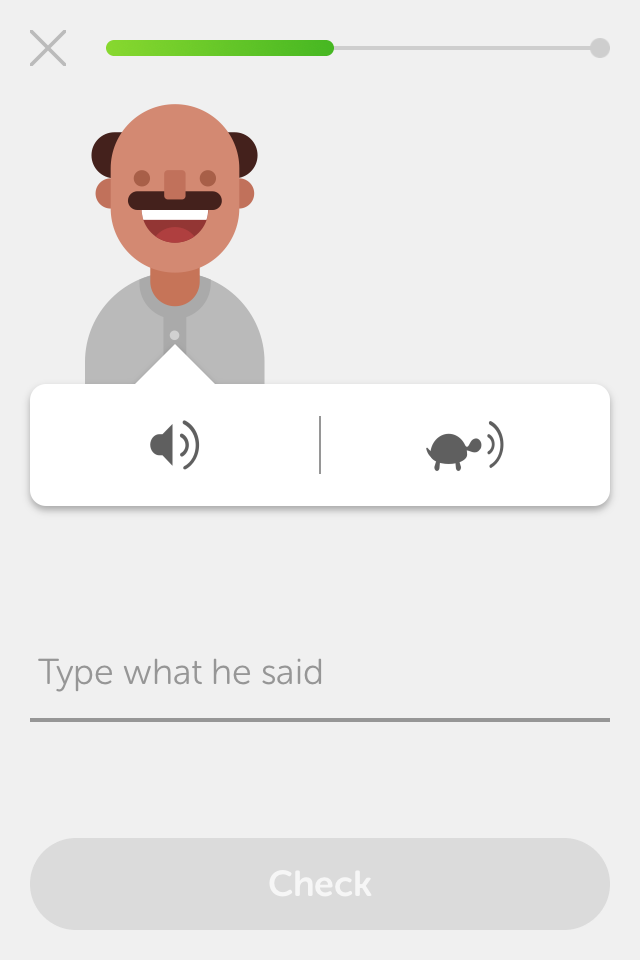
 Slow mode:
Users can choose to hear the audios in a very reduced speed by hitting the turtle icon.
Slow mode:
Users can choose to hear the audios in a very reduced speed by hitting the turtle icon.
Speech recognition
There was no speech recognition feature in the first lessons of the Portuguese course.
Keyboard input
- Typing takes too much time
-
 Typing before learning:
Duolingo often asks users to type in content that has not been introduced.
Typing before learning:
Duolingo often asks users to type in content that has not been introduced.
-
 Typo:
Words with only a few wrong letters are considered correct, and the typo is identified.
Typo:
Words with only a few wrong letters are considered correct, and the typo is identified.
-
 Accents:
Portuguese words typed in without special characters (i.e.: 'é') are considered typos.
Accents:
Portuguese words typed in without special characters (i.e.: 'é') are considered typos.
Other features
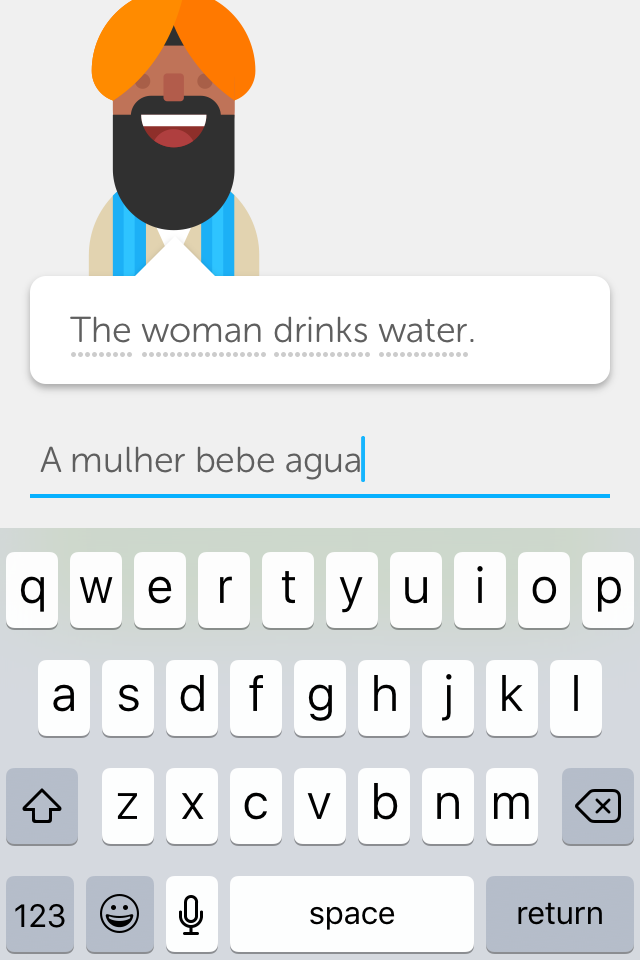
Diversity: Duolingo shows characters from multiple identities, cultures, and ethnicities speaking the user's target language. In this example, it is fascinating that there is a Muslim character represented on Duolingo's Portuguese course, despite the fact that the Muslim population in Brazil is very reduced. By doing that, Duolingo not only shows respect for minorities, but also contributes with the fight against the stereotypification of the Brazilian population.
Conclusions
Duolingo is well-known, cleverly designed, and its game-based exercises are responsive and aethetically pleasant. On the other hand, Duolingo does not offer any significantly new approach from the perspective of language learning. Its whole mechanism is mostly useful to help users memorize small pieces of content by matching words/sentences with their counterparts in the target language. Its most strong design features are the self-efficacy tools, which help users keep track of their progress, create a routine of practice and remain motivated to learn their target languages.